In last post, we have understood what exactly is Metadata Cleanup and why we exactly need it. If you have not read that post, I request you to please read it once to have better understanding for this post. In this post we will see the step by step process to complete Metadata Cleanup.
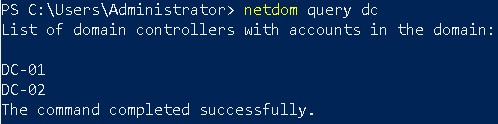
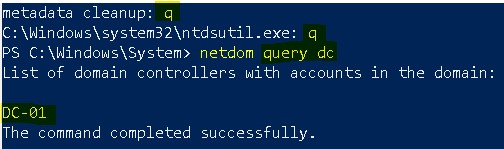
In my lab, I have two domain controllers – dc-01.devopsage.local and dc-02.devopsage.local. To find out the list of domain controllers, run the command netdom query dc.
Now I am assuming that dc-02.devopsage.local is down for any reason and can’t be turned on. This is the DC which I want to clean from my AD environment.
The first thing we will see whether dc-02 is holding any FSMO Role. If yes, you need to seize the role first. To check that, run netdom query fsmo command. In my case, all the FSMO roles are on dc-01, so I can safely proceed for the metadata cleanup of dc-02. We will be using ntdsutil tool.
Login to any of the working domain controller (in my case dc-01) and open the Powershell as Administrator.
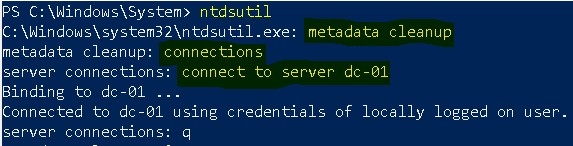
- Run ntdsutil.
- Now under ntdsutil, type metadata cleanup.
- Now type connections.
- Here we first need to connect with a domain controller by running connect to server <server name>. In my case connect to server dc-01.
- It will connect to the given DC. Now type q to come back to metadata cleanup prompt.
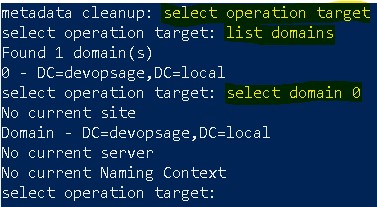
- Now at metadata cleanup prompt, type select operation target.
- Now type list domains. It will give you the list of available domains. In my case I have only one domain, which is showing at sr. no. 0.
- To connect that domain, type select domain <sr. no.>. In my case select domain 0.
- Next step will be to select the site. To find out the available site, type list sites. In my case, I have only one site listed at sr. no. 0.
- To select the site, run a command select site <sr. no.>. In my case, select site 0.
- Now run list servers in site. It will list all the domain controllers on that site. In my case there are two domain controllers – dc-01 and dc-02.
- Note down the sr. no. of the domain controller you want to clean. In my case I want to clean dc-02, which is at sr. no. 1. To select that dc, run command – select server 1.
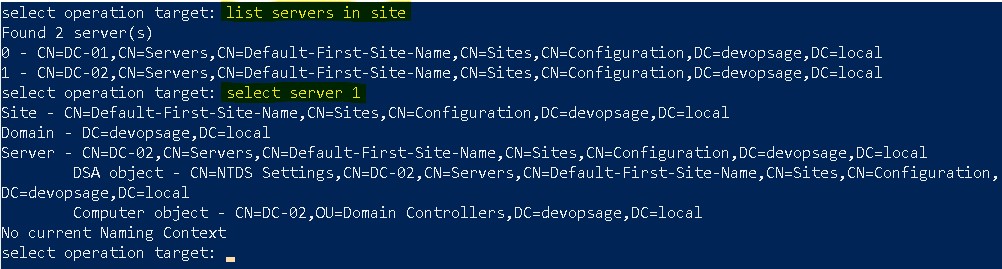
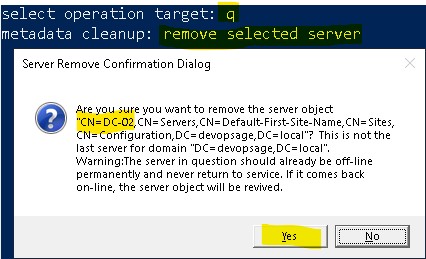
- After server selection, type q to come back to metadata cleanup prompt.
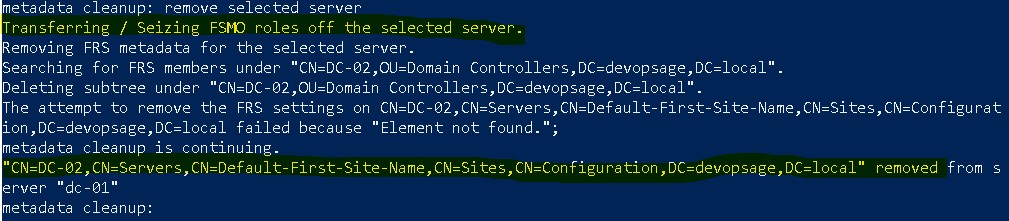
- There run remove selected server command. It will give a pop-up and ask your consent. Verify that correct server is selected and then click on Yes.
It will now proceed with the metadata cleanup. You can also see that it will first try to Seize the available role on that server. At the end, it will give you confirmation for the DC cleanup.
Now you can go to C prompt and check again the list of available DCs. You will find dc-02 is now gone.
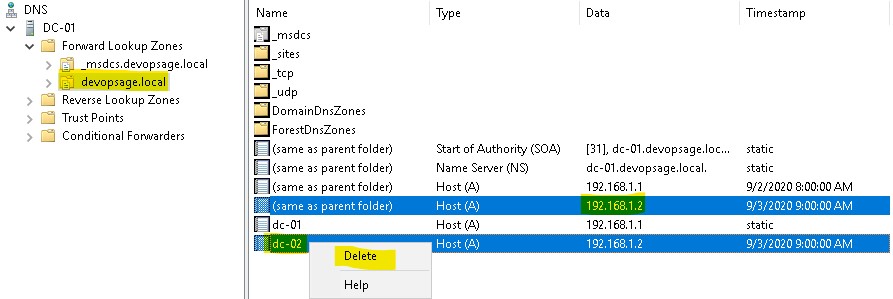
Now you need to delete the A records for dc-02 from the DNS. To do so, open DNS Manager and go to your domain under Forward Lookup Zone. At right pane, you will find the A records of your cleaned DC. Select them all and delete.
The computer account from Active Directory will automatically deleted. However if you want, you can re-verify it in Domain Controllers OU under Active Directory Users and Computers.
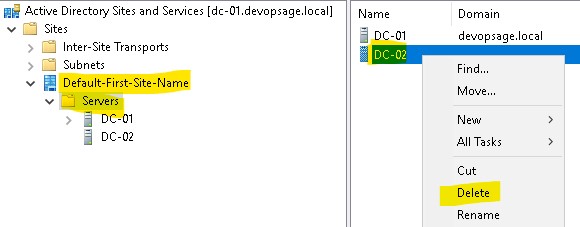
The final step you need to do is to delete the cleaned DC from AD Sites. To do that, open Active Directory Sites and Services and go to Sites -> Default-First-Site-Name -> Servers. There at right pane or below Servers, right click on the cleaned DC (in my case dc-02) and delete it. The site name will also be different in different companies, I am just using it as default.
That’s it! You are done. I hope you found this post informative.